Jet Object
Description
Simulates a wind jet created by a flue in a fipple. It can be used with the 'labium connection to create an oscillating air vortex that excites an air column in a tube to produce a recorder/flute model.
Syntax and Default Values
A Jet object can be created using the following Mlys (Max), mlys.lua, or Lisp syntax:
In Modalys for Max, this object is named mlys.jet:
TODO
TODO
(make-object 'jet
(pressure 1.0)
(air-density 1.2)
(air-speed 340)
(length 0.03)
(width .02)
(height .001)
(flue-labium-distance .004)
(labium-position 2e-4)
(mouth-surface 8e-5))
Parameters
The parameters for this object are a little different from regular objects:
- pressure: pressure controller for the jet.
- air-density: medium density of sound radiation in the propagating medium (kg/m3).
- air-speed / celerity: swiftness/speed of the sound in the propagating medium (m/s).
- length: length of the flue for the jet formation
- width: width of the flue
- height: height of the flue
- flue-labium-distance: distance from the end of the flue to the labium
- labium-position: position of the labium with respect to the flue
- mouth-surface: this is set to 8e-5 by default and does not need to be changed
To simulate propagation in air (room temperature at sea level), you should use an air density value of 1.2 kg/m3 (this parameter is sometimes called rho), and the speed of sound in air, 340 m/s, for air-speed (celerity can be used instead of air-speed for this parameter). The final mouth-surface controller has been documented for completeness but does not need to be provided.
Discussion
The jet object is a special object in Modalys because it implements a nonlinear waveguide model, researched and created by Marc Pierre Verge for his doctoral thesis, instead of the usual modal description model. Consequently it is used is a slightly special way in the Modalys environment.
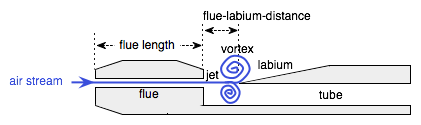
The fipple is the the mouthpiece of a whistle, recorder or other simple flute that generates a jet for sound production. The flue, sometimes also called a duct or “windway,” focuses a jet of air onto the sharp labium - also known as a blade or “windcutter.” The labium itself causes this jet to break into a vortex or whirlpool of air which oscillates back and forth across the labium. The image, above, shows the anatomy of a fipple, with several of its components that relate to this model clearly labeled.
Accesses
The jet is a special object in that it is generally used directly by the 'labium connection, without an access.
In theory you can create accesses at three places on the jet object:
- 'foot
- 'flue-exit
- 'labium
However, for the moment we suggest just using the jet with the 'labium connection, as shown in the simple example script, below:
(setq breath-env (make-controller 'envelope 1 '((0 0) (0.1 100) (1 100) (1.1 0))))
(setq jet (make-object 'jet (pressure breath-env)))
(setq tube (make-object 'closed-open-tube))
(setq tube-acc (make-access tube (const 0) 'long))
(make-connection 'labium tube-acc jet (const 0) (const 4.99 .1 1) (const 0.005))
(setq tube-out (make-access tube (const .9) 'long))
(make-point-output tube-out)
★