WhileLoop : Defining Iteration Conditions
General Properties
 | Whileloop allows a loop to go on as long as a condition is fulfilled . It has only one default input : "expression", which defines a condition. This condition can be expressed by a predicate[1] or any other value connected to the input of whileloop. |
Example : Using Whileloop with a Predicate
A list that contains numbers and letters is enumerated until something else than a number is reached.
| 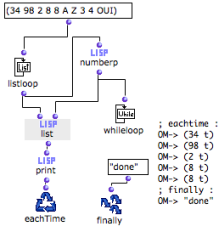 |
- Predicate
A predicate verifies the property of a thing or a relation between two things. It has two possible answers : "true", and "false", that is, "t", or "nil" in Lisp.
