Packages
A package represents a category of programming tools that encloses related functions and classes. It can be organized in sub packages.
Packages of the Library Window
Each package is represented by a small suitcase.
For instance, the Score package contains classes that are literally dedicated to the score domain, such as chords, notes, polyphonies, and functions that can perform operations upon these classes. These packages and their content are "protected" and cannot be modified by the user.
If a package is supposed to contain sub packages, it features an adjacent triangle that allows to open a package on List mode . When this triangle is clicked, the package unfolds and displays its inner sub packages – see below. | 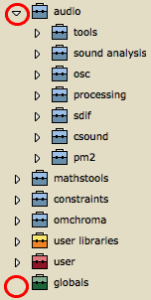 |
Packages Content
A package gives access to both functions and classes of a common "theme", or category of tools. Packages contents can be displayed in List mode, Package mode or Class Tree mode .
The List mode is the sole mode that allows to get a global view of a package whole organization in sub packages. Classes and functions contained in the sub packages cannot be accessed, though. | 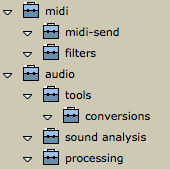 The Midi and Audio packages are open in list mode. We can see their sub packages, but classes and functions cannot be accessed. |
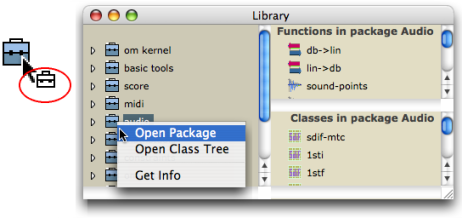
The Package mode allows to access the set of tools contained in a package as a whole : sub packages cannot be visualized.
-
Ctrl/ right click on the suitcase and chooseOpen Package. - Double click on the lower part of the suitcase.
The window extends to display two side panels, respectively containing the package's functions and classes. Their content is refreshed at the selection of another package.
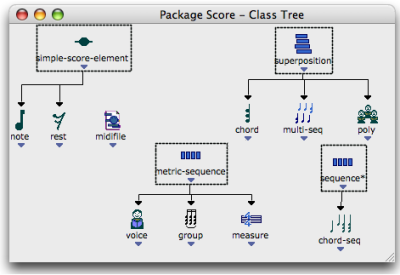
A " class tree " shows the inheritance between the classes of a common package.
| 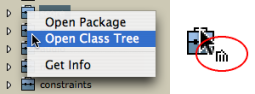 |
The class tree is displayed in a new window. Class trees of the User sub packages can be created and modified graphically.
Using Classes and Functions from the Libary
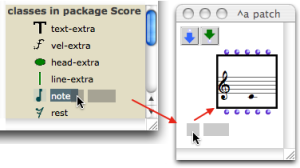 | Tools can be dropped in patches from the library window. |
 Openin the editor of a BPF. | The tools of a package can sometimes be edited. Their content can be displayed in a class or a generic function editor, which opens with a double click on the class or function's icon. |
To obtain information about a select package, class or function of the library, use the Info window :
-
Ctrl/ right click on an item and chooseGet Info - select
File / Get Info -
press
Cmd+i.
Information related to the items of the User package can be edited.
- Class
A category of objects sharing common properties – characteristics and behaviour. A class specifies the internal structure and behaviour of an object. In OM, it is represented in a patch by a factory box that can produce an instance of a class.
See also : Object, Instance
- Function
A portion of code within a larger program, which performs a specific task. Operates upon 0 or more parameters and returns a value.
- Global variable
An instance of OM object that has been saved in order to be used in other programs. Global variables are visible from the
Librarywindow and stored as .omi files in theGlobalsfolder of the workspace.
