Inputs and Outputs
A function box has a number – 0 or more – of inputs, which represent the arguments1 of the function, and one or more outputs, which return the result(s) of a computation.
Inputs
The inputs of a box initially come with default values. Nevertheless, they seldom enable correct computations : their values must be reset by the user or they must be connected to other boxes' outputs.
| 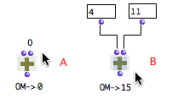 An addition with and without the default values of OM+ |
Default values can be set directly when typing the name of the function box – for instance : "om+ 5 7". | 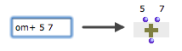 |
 | Information is provided by tooltips or in the available documentation. |
Outputs
Outputs can be evaluated and used for connections with other boxes. Hence, one can evaluate either a whole function, or a specific output that may return a different result.
- To evaluate a function box, elect it and press
v. -
To evaluate a specific output,
Cmdclick on it.
The result of the computation is given instantly in the Listener2 window.
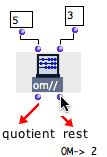 Om// performs an euclidean division : its first output returns a quotient, its second output returns a rest. The evaluation of the "rest" output necessarily triggers the evaluation of the whole function. | A function box may have several outputs, which means that it can return multiple values.
|
Each output can be connected and/or evaluated independently, which doesn't affect the behaviour of the function. | 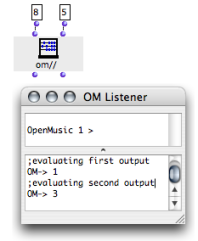 The outputs of om// have been evaluated successively. |
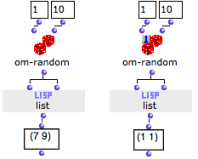 Om-random returns a random number between a minimum and a maximum value. | The " evaluate-once " mode is generally useful for multiple outputs function boxes : the result of a same evaluation is sent to all connected boxes. Otherwise, each of them will evaluate the function box separately :
Here, in the first case, om-random is on the standard evaluation mode and returns two different results to each input of list, as shown in the text box below. In the second case, it returns the same result. |
- Argument
An argument represents a parameter upon which a function operates. For instance, the (om+ x y) function has two arguments : x and y.
- Lisp Listener
A Lisp communication interface displaying results of computations, warnings or error messages, and where Lisp expressions – programs – can be evaluated.
