OMif : If, Then, Else
The behaviour of omif can be described by the following proposition : "IF the A condition is verified, THEN execute the B operation, ELSE execute the C operation".
The omif box can be accessed via the Functions / Kernel / Control / OMIF menu (or typing "OMIF" in the patch window).
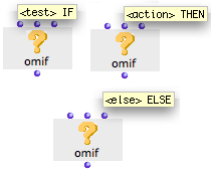 | Omif has two default inputs and one optional input :
Each input accepts a function, a factory, or a data box. |
To add or delete the optional "else" argument : press Alt +← or → / SHIFT + > or <.
"Test" evaluates the box it is connected to and checks if a number of conditions for the operation are fulfilled.
- If the box yields something else than "nil", the conditional test is verified, and " then" evaluates the box connected to its second input.
- It the box yields "nil", OMIF returns the same "nil" value.
Omif is evaluated like any other box, and returns the value yielded by "then" or "else".
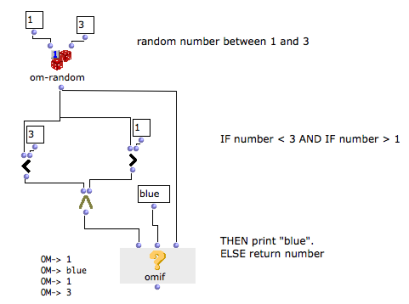
Here, "test" evaluates the om= predicate, which checks if the value returned by om-random is equal to 2.
| 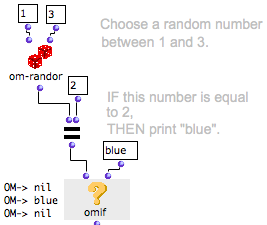 |
Here, "test" is determined by the om= predicate, but it can also be connected to any other type of box.
In this example, "else" has been added to OMIF. If the condition is not fulfilled, OMIF doesn't return "nil", but the random number.