Class-Array Object
The
class-array
box is accessed via the Classes / Basic Tools / Array menu.
Properties
The class-array box has a number of columns , called " components " and a variable number of rows or lines , called " fields ".
 | The class-array box has two default inputs and outputs
|
The class-array can be added a number of keyword arguments , which represent the fields of the matrix. Each keyword input has a corresponding output. | 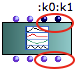 |
Rows and Columns
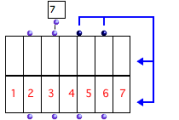 An empty class-array with 2 fields – rows – and 7 components – columns. | Each column represents a component . Each line or row in the matrix display represents a field , which corresponds to one of the keyword inputs of the box.
|
The class-array is designed to be used as a superclass for array classes with default fields.
Subclasses[1] can be created either with Lisp code, or visually in OMExamples of class-array subclasses are the classes from the OMChroma system for the control of sound synthesis.
By default, keyword inputs – additional fields – are called ":k1", ":k2", etc...
To modify these names :
1. click on the input
2. enter a name starting with ":"
The value of keyword inputs must come from a connected box.
Instantiation
The class-array has an original and powerful instantiation system that interprets the input data connected to its different filed inputs automatically. If needed, input data is converted to generate and fill all the components values internally, depending on the given number of columns.
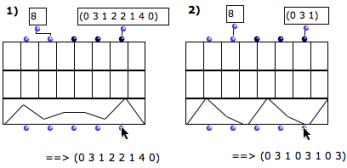
The list fits the number of components. The items contained in each list are assigned to the successive components.
If the number of items is superior to the number of components, the list is repeated.
A single value is repeated for every component of the array. | 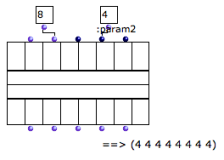 The constant value is repeated for all the components. |
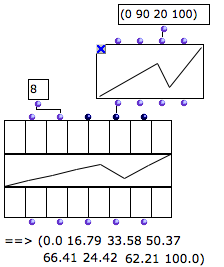 Eight values are sampled periodically in the curve. | A BPF can be resampled according to the number of components of the class-array . Hence, each component can be assigned a value , no matter how many points the BPF has. This class-array contains eight components, or columns.
Note that using the "x-points" or "y-points" instead of the "self" output of the BPF amounts to feeding the array with a list of value. |
If a function or a box on "lambda" mode is connected to a field of the array, it is applied to the components of the field at the evaluation. Here, arrays # 1 and 3 are instantiated with two functions :
| 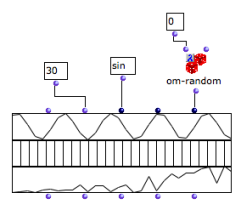 Instantiating arrays with the sinus and om-random functions. |
Creating Arrays with Objects
Objects, such as notes , chords , or any object in OM, can also be used for filling the matrix fields. These objects must be connected as a list to the class-array inputs.
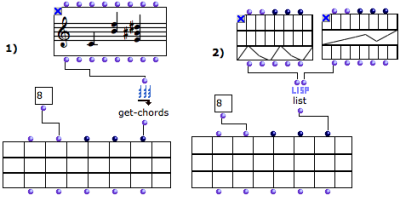
This procedure also allows, for instance, to create arrays of arrays, as in example 2 above.
In class-array subclasses , the type of a subclass field may change the way input data is interpreted.
- Subclass
A subclass is derived from a preexisting class, by inheritance. In object-oriented programming, objects are defined by classes. New objects can be created from existing objects. As objects are defined by classes, classes can inherit other classes. Sub-classes inherit attributes and behavior of the pre-existing classes, or super-classes. Code is compartmentalized and reused by creating collections of attributes and behaviors called objects which can be based on previously created objects.
