Boxes Morphology
This section deals with function boxes and factory boxes1. A factory box represents a class of objects in a program, such as notes, sounds, rhythms. A function box refers to a function that is designed to perform an operation upon objects.
Main Layout
All boxes have :
| 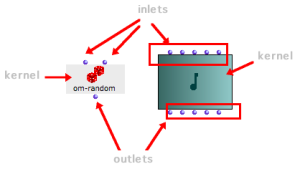 |
Inlets and outlets are used for connecting boxes. They are represented by small blue balls and located on the upper and lower parts of the box. Each of them is assigned a specific parameter that characterizes the function2 or the class3 the box refers to.
Several functions or factory boxes belonging to a same category of operators often share the same icon. Factory boxes are often characterized by a blue-green background layer. | 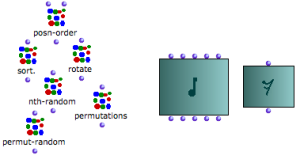 Function boxes and factory boxes belonging to the "combinatorial" and "score" categories. |
The name of factory boxes is not displayed by default. A number of simple functions – such as om+, om-, om/ ... show no name.
Additional Characteristics
A small label located on the upper left corner of the box can show the possible evaluation4 mode of a box. Evaluation modes are used for controlling the transmission of resulting data in a program, or for performing specific tasks . | Boxes on lock mode : computed values can't be changed. |
|
|
All boxes have an invisible square resizing area in their bottom-right corner. |
Changing Boxes Appearance
The default size and font of boxes can be modified via the General Preferences tab ![]() via the
via the OM 6.x.x / Preferences menu.
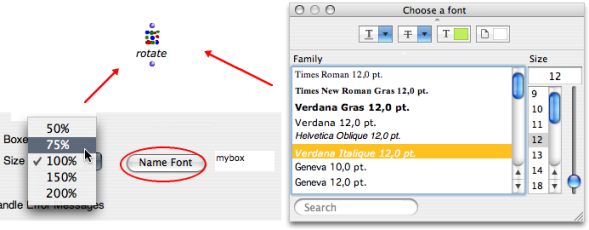
- To change the default size, select a resizing rate in the
Boxes Sizepop up menu. - To change the name font, click on
Name Font, choose a font in the pop up window.
Press Apply and/or OK to validate the modifications.
- Factory Box
A box used for creating an instance, or exemplar, of a given class within a visual program.
- Function
A portion of code within a larger program, which performs a specific task. Operates upon 0 or more parameters and returns a value.
- Class
A category of objects sharing common properties – characteristics and behaviour. A class specifies the internal structure and behaviour of an object. In OM, it is represented in a patch by a factory box that can produce an instance of a class.
See also : Object, Instance
- Evaluation
Triggers the calculus that will determine the value of an expression. Applies to functions and objects.
⤷ Click and press
vorCmdclick on an outlet.
