Class Input Slots
The OMChroma's classes are accessible in two ways :
- via the Library window
- typing the box's name directly in the patch editor
Library Window
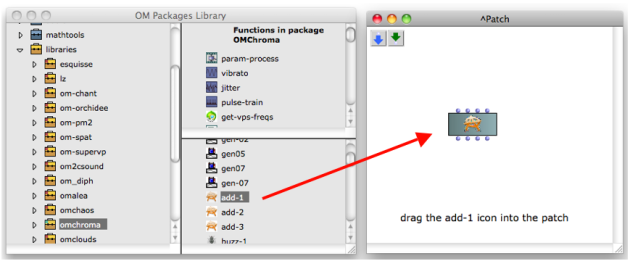
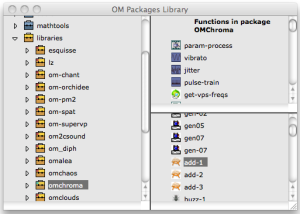
omchroma in the OM Packages Libraries in the Library window contains the available OM classes and functions organized in thematic sub packages.
Open the Library window
Select omchroma, click on it and press enter to open the classes and functions windows.
Drag and drop the function or the class icon into the patch editor.
Adding a Box Directly to the Patch Editor
The name of a class or function can always be keyed in a patch editor directly.
|  |
Input Slots
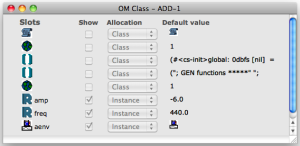
The OMChroma Class has two types of input slots
| 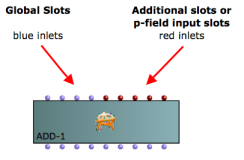 |
The 4 global slots are always visible and with blue inlets. From left to right they are :
Name | Description |
|---|---|
self | Synthesis event |
numcols | Number of components |
action-time | Event offset(s) |
user-fun | A lambda function applied to each component |
The Additional slots are not directly showed. To make them appear select the class and type shift + arrow key.
The first two inlets from the left are always the same for every class of a Csound orchestra, that is :
Name | Description |
|---|---|
e-dels | Entry delays [sec], time interval between the object's "action-time" and the beginning of each line in the score. |
durs | Duration [sec], duration of each line in the score. |
The other slots can be many and have their own name according to the requested data.
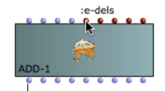 | To see the ScreenTip with the description of the slot point the arrow on it. |
Types of Input Data
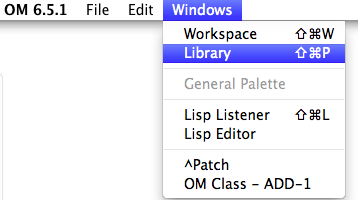
Select the OMChroma Library and click on it and press enter to open the classes and functions panels. |
Take a close look at the icons of the slots.
The p-fields with this kind of icon allow only numbers (of any kind). |
The p-fields with this kind of icon allow only BPF or numbers which refer to a Csound GEN function. Their name always ends with "env" (ex. aenv). |
More About GEN Functions in Csound
Csound uses lookup tables for many purposes. These function tables (f-tables) contain everything from periodic waveforms to other kind of data. The specific data are created with Csound's f-tables generator subroutines, or GEN routines. A Csound f-table is an array of floating point values stored in RAM to be used while Csound computes sound. These f-tables are usually defined in the Csound score file and are often restricted to a size of a power of two (2n) or a power of 2 plus one (2n + 1). Tables can be visually displayed as mathematical graphs with data addresses plotted from left to right along the x-axis and the actual stored data plotted along the y-axis.
Description of the parameters of the f-statement (or Function Table Statement).
Syntax
f p1 p2 p3 p4 p5 ...
Performance
p1 Table number by which the stored function will be addressed.
p2 Action time of the function generation.
p3 Size of the function table (it must be a power of 2, or a power-of-2 plus 1).
p4 Number of the GEN function to be called.
p5 Parameters whose meaning is determined by the particular GEN routine.
Example
p1 | p2 | p3 | p4 | p5 | p6 | p7 | p8 | p9 |
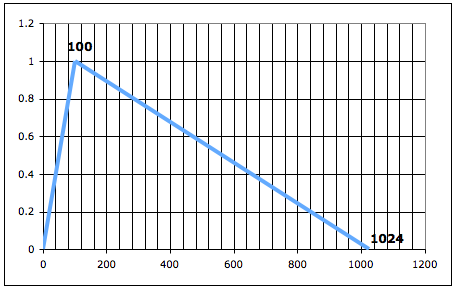
f100 | 0 | 1024 | 7 | 0 | 124 | 1 | 900 | 0 |
p1 = 100 (number of the table, i.e. the number 100 will identify this table)
p2 = 0 (action time of function generation; here, it is at time 0 of the score)
p3 = 1024 (size of the table, i.e. number of points, 210)
p4 = 7 (the GEN function number 7 is similar to a BPF, as it draws linearly interpolated segments between specified points)
p5 = 0 (y-axis value at 0 x-axis value)
p6 = 124 (x-axis distance from the previous point, that is 124 points after the beginning)
p7 = 1 (y-axis value at p6 x-axis value)
p8 = 900 (x-axis distance from the previous point, that s 900 points after p6)
p9 = 0 (y-axis value at p8 x-axis value)
NB: the sum of all the x-axis distances should equal the table's size, otherwise the table will be padded with zero's or truncated (if the sum is, respectively, smaller or larger).
Graph of the f-table # 100
Special cases
Normally, the y-values are normalized between 0 and 1 when Csound instanciates the table. However, a negative GEN number implies that the function is not rescaled, and maintains its original values.
GEN function number 1 transfers data from a soundfile into a function table and is therefore used with samplers. Its size is ordinarily a power of 2 or a power-of-2 plus 1; the maximum tablesize is 16777216 (224) points. The allocation of table memory can be deferred by setting this parameter to 0; the size allocated is then the number of points in the file (probably not a power-of-2), and the table is not usable by normal oscillators, but it is usable by a loscil unit. The soundfile can also be mono or stereo. The OMChroma classes smpl-3 to smpl-6 use deferred tables.
- OMChroma User Manual
- System Configuration and Installation
- Getting started
- Class Input Slots
- Slots' Description and Default Values
- Amplitude and Internal Editor
- Amplitude Envelope
- f-GEN Reserved Numbers
- Audio Waveforms
- Chord-seq to OMChroma
- Spectrum Chord and Arpeggio
- Velocity versus Amplitude
- Exponential Amplitude Envelope with a BPF
- Relationship with the Csound .orc and .sco files
- Slots polymorphism
- Managing GEN function and sound files
- Predefined Classes
- User-fun
- Creating a new Class
- Multichannel processing
- Appendix A - Common Red Patches