Reading and Writing Files
StreamFile : a Pointer to Read and Write Files
The StreamFile box represents the file to read or write during the File-Box process. It is attached to the file via its pathname.
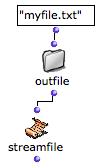 | It has one input and one output :
|
The properties of the StreamFile can be edited if needed.
To open the StreamFIle properties window, double click on the box.
- Three options are offered a the top of the window : Read / Write, Write, Read.
- The pop up menu offers two file formats : text or SDIF.
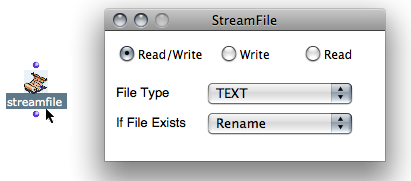
The pop up menu offers four options, which apply to the targeted file if it exists. Each of the different options determine the way the program behaves when the text file is open or created to access its contents and the choice of a destructive or non destructive action.
- " Rename " : the existing file is renamed and a new file is created.
- " Supersede " : the existing file is superseded; that is, a new file with the same name as the old one is created. The old file is deleted.
- " Overwrite " : the file is not deleted but modified with the input data. For instance, if an existing file contains ten lines, and that the new data represents three lines, the three first lines of the existing file are replaced.
- " Append " : the new data is added after the ending of the previous content of the file.
Writing Contents
The file-write function writes something in the file. It has two inputs and one output:
| 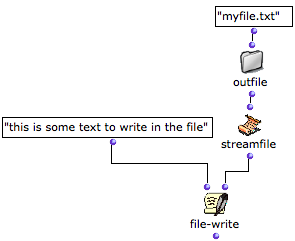 |
The file-write-line function is similar to file-write, but adds a line return at the end of the input data.
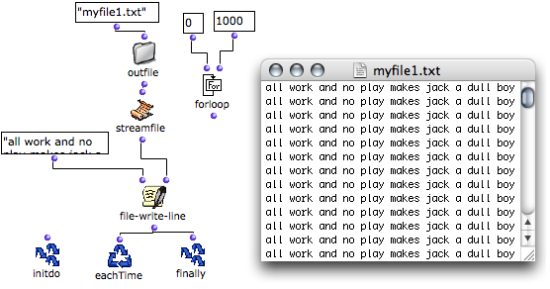
To write several lines, an iterative process must be introduced in the program. Most of the time, each iteration triggers one operation in the File-Box loop.
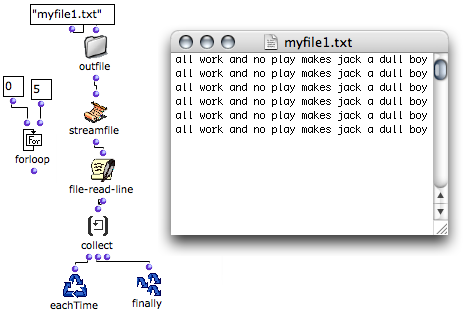
Reading Data from a File
The file-read-line function allows to read one line in a file. It has one input and one output :
When all the lines of the text are exhausted, file-read-line returns "nil". |  |
Most of the time, each iteration triggers one operation. In this case, the successive lines can be stored with an accumulator such as collect, as in an OMLoop.
"Eof" stands for "end of file", "p" for "predicate". The file-eof-p function is a predicate, which tests if a streamfile is at the end of the file. It has one input and one output :
It can be associated with whileloop and OMIF, which execute a specific operation when the end of the file has been reached. Hence, this function allows to read a file whose number of lines is unknown. | 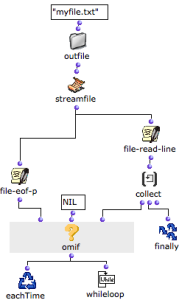 As long as the predicate finds no streamfile, it returns "nil", and lines are collected. |
