Score Classes
 | Score classes enclose the musical objects that compose a score : notes , chords , chord-seqs , voices , polys . Out of convenience, we have gathered these objects in three categories : "harmonic", "rhythmic" and "polyphonic" objects. They can be accessed via the menu. |
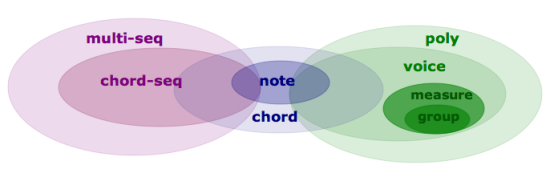
Types : "Harmonic", "Rhythmic" and "Polyphonic" Objects.
-
Harmonic objects include notes , chords and chord-seqs .
-
Rhythmic objects include voices (internally made of measures and groups).
-
Polyphonic objects include polys and multi-seqs . These are "superimpositions" of objects :
- voices on one hand,
- chord-seqs on the other hand.
Time Representation
These objects can be classified into two temporal categories :
- Pulsed, or rhythmic representations are based on a traditional rhythmic expression of events in time, via rhythm trees1. Voices and polys are pulsed representations.
- Linear representations are based on the absolute duration of events – in milliseconds. Chord-seqs and multi-seqs are linear representations.
- Notes and chords are atomic objects and correspond to both temporal categories.
- Rhythm Tree
A rhythm tree expresses a rhythmic structure as a list.
This list is made of :
-
a duration, or number of measures,
-
a list of measures.
Each measure is made of
-
a time signature
-
a list or proportions, or rhythmic values.
For instance : (1 (((4 4) (1 1 2))) is a rhythm of one measure, signature 4/4, with two quarter and one half note (proportions = 1/4 1/4 2/4 = 1/4 1/4 1/2).
The term of "tree" refers to a recusrive structure: each item in the proportions list can in turn be expressed as a duration with a list of subdivisions.
For instance the second beat in our measure could be subdivided as follows : ((4 4) (1 (1 (2 3)) 2)).
-
