Frequency Shift
Constant Frequency Shift
With frequency shifting, a a constant value is added to the frequency of each component of a signal, so that (harmonic) relationships between signal components are not preserved. If a signal is shifted up by 1.5KHz, the resulting signal will have components whose frequencies are 2.5KHz, 3.5KHz, and 6.5KHz. We have seen that the manipulation of time/frequency regions allow to shift portions of spectrum – snippets – instead of transposing them, but this is done unilateraly. In AS, frequency shift also exist as a treatment, and can be applied with a constant value, or dynamically.
 | To apply a frequency shift to an open soundfile, choose An elementary dialogue window will open. |
Specify a constant shift value in the prompt Press | 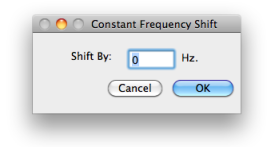 |
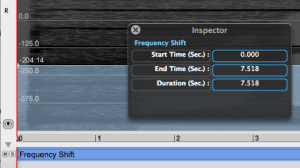
A blue BPF will appear in the sonogram window, with the constant value displayed on the left. The Inspector window will show :
The constant value of the BPF is displayed on the left, with a scale and grid corresponding to the maximum and minimum displayed values specified in the Inspector. |
Dynamic Frequency Shift
Once a constant value has been specified, the BPF can be edited like any other BPF.
To modify its parameters, select the first point or add new points. The parametric values will be displayed in the Inspector and can be modified according to the usual procedures
A horn, playing a 260 Hz C3 is frequency shifted with changing values, which can be in harmonic relationship or not with the fundamental. The sonogram analysis shows that the original harmonic relationship is not preserved. When the value is a multiple of the original F0, the result is rather harmonic. When not, the sound becomes close to the produce of a frequency modulation.
- Introduction
- About this Document
- Introduction
- Installation
- Going Through an AS Session
- The AudioSculpt Environment
- Signal Representation
- Signal Analysis
- Modeling Sounds with Sinusoids
- Signal Manipulation
- Managing Treatments
- Processing Sequencer
- Advanced Use
- Errors and Problems
- Basic Analysis/Synthesis Notions